11 塗り:フィル, ストローク, 色, ペイントサーバ
目次
11.1 概要
テキスト内容要素
と
図形
を含む
グラフィックス要素
には、フィル( fill - オブジェクトの内部への塗り)とストローク( stroke - オブジェクトの外形線への塗り)を行える。フィルとストロークはより一般的な用語の塗り操作と考えることができる。
Graphics elements, including text content elements and shapes, can be filled (which means painting the interior of the object) and stroked (which means painting along the outline of the object). Filling and stroking both can be thought of in more general terms as painting operations.
SVG においては次による塗り(すなわちフィルまたはストローク)ができる:
With SVG, you can paint (i.e., fill or stroke) with:
-
透明度も持ち得る、単色
a single color, possibly with some level of transparency
-
グラデーション(線型または放射型)
a gradient (linear or radial)
SVG はペイントサーバという概念を用いる。システムペイントを除き、ペイントサーバは
fill
あるいは
stroke
プロパティの
局所 IRI 参照
を用いて指定される。グラデーションや色は特定の種類のペイントサーバになる。
SVG uses the general notion of a paint server. Apart from system paint, paint servers are specified using a local IRI reference on a 'fill' or 'stroke' property. Gradients and colors are just specific types of paint servers.
11.2 塗りの指定
fill
および
stroke
プロパティは
<paint>
型の値をとり、次のように指定される:
Properties 'fill' and 'stroke' take on a value of type <paint>, which is specified as follows:
- none
-
塗りを適用しないことを指示する。
Indicates that no paint shall be applied.
- currentColor
-
color
プロパティの現在のアニメーション値により指定される色を用いて塗りを適用するものとすることを指示する。この仕組みは、他の(非 SVG )XML などの親の言語との色属性の共有を容易にするために提供されている。これにより、 HTML で定義した
color
プロパティの設定を含むスタイル付けを
SVG-UA
に渡して SVG テキストを HTML と同じ色で描画させられるようになる。
Indicates that painting shall be done using the color specified by the current animated value of the 'color' property. This mechanism is provided to facilitate sharing of color attributes between parent grammars such as other (non-SVG) XML. This mechanism allows you to define a style in your HTML which sets the 'color' property and then pass that style to the SVG user agent so that your SVG text will draw in the same color.
-
<color>
-
明示的な( sRGB 色空間
[SRGB]
内の)
色
。
the explicit color (in the sRGB color space [SRGB]).
-
<FuncIRI>
[ none | currentColor |
<color>]
-
<FuncIRI>
はグラデーションなどの
ペイントサーバ
指定する。
<FuncIRI>
の素片識別子は現在のオブジェクトの塗りに適用されるものとするペイントサーバ(
グラデーション,
solidColor
など)へのリンクを与える。
SVG Tiny 1.2 UA
には
局所 IRI 参照
のサポートのみが要求される。
IRI 参照
が
無効
なものであった場合(例えば、存在しないオブジェクトや有効でないペイントサーバを指していたり、
非局所 IRI 参照
でビューアがそれをサポートしていない場合)、予備の値が指定されていればそれが利用されるが、そうでない場合は none が指定されたものとして扱われなければならない。
The <FuncIRI> specifies a paint server such as a gradient. The fragment identifier of the <FuncIRI> provides a link to the paint server (e.g., a gradient or 'solidColor') that shall be used to paint the current object. SVG Tiny 1.2 user agents are only required to support local IRI references. If the IRI reference is invalid (for example, it points to an object that doesn't exist or the object is not a valid paint server or it is a non-local IRI reference and the viewer does not support it), then the fallback value (if specified) is used; otherwise it must be treated as if none was specified.
- <system paint>
-
システムペイントサーバ
A system paint server
11.3 フィルプロパティ
fill
プロパティは与えられたグラフィカルな要素の内部への塗りを定める。塗られる領域は図形の外形線の内側の領域すべてからなるものとする。図形の内側の決定においては、すべての部分パスが考慮に入れられなければならず、
fill-rule
プロパティの値で指定される規則に従うものとする。幾何学的に幅0の図形の外形線は塗り領域に含まれなければならない。
The 'fill' property specifies that the interior of the given graphical element must be painted. The area to be painted shall consist of any areas inside the outline of the shape. To determine the inside of the shape, all subpaths must be considered, and the interior shall be determined according to the rules associated with the current value of the 'fill-rule' property. The zero-width geometric outline of a shape must be included in the area to be painted.
開いた部分パスに対しては、その両端をつなげるように "closepath" 命令が追加されたものとみなした上でフィルが行われなければならない。従って、フィル操作は
path
要素内の開いた部分パス(すなわち closepath 命令の無い部分パス)と
polyline
要素のいずれにも適用される。
Open subpaths must be filled by performing the fill operation as if an additional "closepath" command were added to the path to connect the last point of the subpath with the first point of the subpath. Thus, fill operations apply to both open subpaths within 'path' elements (i.e., subpaths without a closepath command) and 'polyline' elements.
-
'fill-rule'
-
| 値: |
nonzero | evenodd |
inherit
|
| 初期値: |
nonzero |
| 適用対象: |
図形,
テキスト内容要素
|
| 継承: |
する |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
fill-rule
プロパティは、
キャンバス
のどの領域を図形の内側にするかを決定する際に利用しなければならないアルゴリズムを指示する。単純な交点のないパスの場合はどの領域が内側になるのかは直感的に明らかであるが、自身が交わるパスや部分パスが他の部分パスを囲むときのような、より複雑なパスにおける「内側」の解釈はそれほど自明なことではない。
The 'fill-rule' property indicates the algorithm which must be used to determine what parts of the canvas are included inside the shape. For a simple, non-intersecting path, it is intuitively clear what region lies "inside"; however, for a more complex path, such as a path that intersects itself or where one subpath encloses another, the interpretation of "inside" is not so obvious.
fill-rule
プロパティに指定できる図形の内側の決定方法には2つの選択肢がある:
The 'fill-rule' property provides two options for how the inside of a shape is determined:
- nonzero
-
キャンバス
上の点が「内側」にあるかどうかの決定には、次の手順あるいは同じ結果を出す他のものを用いなければならない。点から任意の方向へ無限遠まで伸びる射線を引き、その射線と図形のパスが交わる所を吟味する。パスが点から見て射線の左から右へ交差するときは 1, 右から左へ交差するときは -1 と数える。その総和が 0 のとき点はパスの外側、他の場合は内側にあるものとする。次の図に nonzero 規則を示す:
The following algorithm, or any other that gives the same result, must be used to determine the "insideness" of a point on the canvas. Draw a ray from the point to infinity in any direction and then examine the places where a segment of the shape crosses the ray. Starting with a count of zero, add one each time a path segment crosses the ray from left to right and subtract one each time a path segment crosses the ray from right to left. After counting the crossings, if the result is zero then the point is outside the path. Otherwise, it is inside. The following drawing illustrates the nonzero rule:
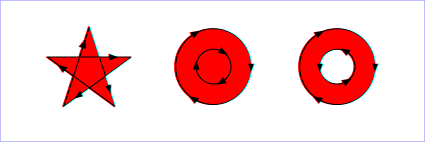
この例を SVG として表示( SVG 対応ブラウザのみ)
- evenodd
-
キャンバス
上の点が「内側」にあるかどうかの決定には、次の手順あるいは同じ結果を出す他のものを用いなければならない。点から任意の方向へ無限遠まで伸びる射線を引き、その射線と図形のパス区分との交点を数える。その総和が奇数なら内側、偶数なら外側にあるものとする。次の図に evenodd 規則を示す:
The following algorithm, or any other that gives the same result, must be used to determine the "insideness" of a point on the canvas. Draw a ray from the point to infinity in any direction and counting the number of path segments from the given shape that the ray crosses. If this number is odd, the point is inside; if even, the point is outside. The following drawing illustrates the evenodd rule:
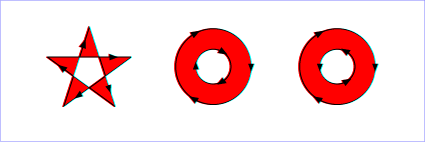
この例を SVG として表示( SVG 対応ブラウザのみ)
(注記:上の説明ではパスの一部が射線の一部と合致するときやパスが射線と接するときにどうするかを指定していないが、射線の選び方は任意であるので、単にこのような交接の無い射線を選び直せばよい。)
(Note: the above explanations do not specify what to do if a path segment coincides with or is tangent to the ray. Since any ray will do, one may simply choose a different ray that does not have such problem intersections.)
fill-opacity
は現在のオブジェクトの内部への塗り操作に用いるものとする不透明度を指定する(
図形とテキストの塗り
を見よ)。
'fill-opacity' specifies the opacity of the painting operation which shall be used to paint the interior the current object. (See Painting shapes and text.)
- <opacity-value>
-
現在のオブジェクトのフィルにおける塗り操作に用いる不透明度。 0.0 (完全透明)から 1.0 (完全不透明)までの範囲の外の値はこの範囲に切り上げ/下げされる(
特定の範囲への値の切り上げ/下げ
を見よ)。
The opacity of the painting operation that is to be used to fill the current object. Any values outside the range 0.0 (fully transparent) to 1.0 (fully opaque) must be clamped to this range. (See Clamping values which are restricted to a particular range.)
関連するプロパティ:
stroke-opacity
。
Related property: 'stroke-opacity'.
11.4 ストロークプロパティ
以下では要素がどのようにストロークされるかに影響するプロパティについて述べる。
The following are the properties which affect how an element is stroked.
いかなる場合においても、ダッシュパターン(dash pattern - 点線)を持つものなど、方向に影響されるどのストロークも、
グラフィックス要素
の開始点と同じ点からストローク操作が開始されたかのように描画されなければならない。特に、
path
要素におけるパスの開始点は最初の "moveto" 命令の最初の点である。
In all cases, strokes which are affected by directionality, such as those having dash patterns, must be rendered such that the stroke operation starts at the same point at which the graphics element starts. In particular, for 'path' elements, the start of the path is the first point of the initial "moveto" command.
ストロークにおいては、ダッシュパターンの様な
グラフィックス要素
の外形線に沿う進行に依存する計算における距離計算には SVG-UA の標準の
パスに沿う距離
のアルゴリズムを利用することが要求される。
For strokes, such as dash patterns whose computations are dependent on progress along the outline of the graphics element, distance calculations must use the SVG user agent's standard distance along a path algorithms.
グラデーションの様な複雑なペイントサーバを利用するストローク操作による結果は、現在の
グラフィックス要素
とそれに結び付けられたストロークプロパティにより定義される幾何学的図形が幾何学的に同値な
path
要素に変換された上で、与えられたペイントサーバによるフィル操作が行われた場合の結果と一致していなければならない。
When stroking is performed using a complex paint server, such as a gradient, the stroke operation must be identical to the result that would have occurred if the geometric shape defined by the geometry of the current graphics element and its associated stroking properties were converted to an equivalent 'path' element and then filled using the given paint server.
stroke
プロパティにより、与えられた
グラフィックス要素
は外形線に沿って塗られるものとする。
The 'stroke' property shall paint along the outline of the given graphics element.
1個の
moveto
命令のみからなる部分パス(
パス
を見よ)はストロークされないものとする。1個の
moveto
命令と同じ点への
lineto
命令のみからなる部分パスや、1個の
moveto
命令と1個の
closepath
命令のみからなる部分パスは
stroke-linecap
プロパティが butt に設定されているときはストロークされないものとし、
stroke-linecap
プロパティが round または square に設定されているときは、与えられた点を中心とする円または正方形(同順)を生成するストロークが行われるものとする。
A subpath (see Paths) consisting of a single moveto shall not be stroked. A subpath consisting of a moveto and lineto to the same exact location or a subpath consisting of a moveto and a closepath shall not be stroked if the 'stroke-linecap' property has a value of butt and shall be stroked if the 'stroke-linecap' property has a value of round or square, producing respectively a circle or a square centered at the given point.
このプロパティは要素の
装飾付き包含ボックス
に寄与する。
This property contributes to an element's decorated bounding box.
-
<length>
-
現在のオブジェクトに利用するものとするストロークの幅。値が0の場合はストロークされないものとする。負値は
サポート外
であり、ストロークは指定されなかったものとして扱われなければならない。
The width of the stroke which shall be used on the current object. No stroke shall be painted for a zero value. A negative value is unsupported and must be treated as if the stroke had not been specified.
このプロパティは要素の
装飾付き包含ボックス
に寄与する。
This property contributes to an element's decorated bounding box.
-
'stroke-linecap'
-
| 値: |
butt | round | square |
inherit
|
| 初期値: |
butt |
| 適用対象: |
図形,
テキスト内容要素
|
| 継承: |
する |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
stroke-linecap
はストロークの際に開いた部分パスの両端に利用する形状を指定する。
'stroke-linecap' specifies the shape which shall be used at the end of open subpaths when they are stroked.
- butt
-
開いた部分パスの両端には下の図に示すような図形を描くものとする。
The shape drawn at the end of open subpaths shall be as per the drawing below.
- round
-
開いた部分パスの両端には下の図に示すような図形を描くものとする。
The shape drawn at the end of open subpaths shall be as per the drawing below.
- square
-
開いた部分パスの両端には下の図に示すような図形を描くものとする。
The shape drawn at the end of open subpaths shall be as per the drawing below.

この例を SVG として表示( SVG 対応ブラウザのみ)
このプロパティは要素の
装飾付き包含ボックス
に寄与する。
This property contributes to an element's decorated bounding box.
-
'stroke-linejoin'
-
| 値: |
miter | round | bevel |
inherit
|
| 初期値: |
miter |
| 適用対象: |
図形,
テキスト内容要素
|
| 継承: |
する |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
stroke-linejoin
は
図形
ストロークにおいて角【(パス区分の継ぎ目)】に利用する形状を指定する。
'stroke-linejoin' specifies the shape which shall be used at the corners of shapes when they are stroked.
- miter
-
パスの角には下の図に示すような
図形
を描くものとする。
The shape drawn at the corner of shapes shall be as per the drawing below.
- round
-
パスの角には下の図に示すような
図形
を描くものとする。
The shape drawn at the corner of shapes shall be as per the drawing below.
- bevel
-
パスの角には下の図に示すような
図形
を描くものとする。
The shape drawn at the corner of shapes shall be as per the drawing below.

この例を SVG として表示( SVG 対応ブラウザのみ)
このプロパティは要素の
装飾付き包含ボックス
に寄与する。
This property contributes to an element's decorated bounding box.
2つの線分の継ぎ目が鋭角になっている状況で
stroke-linejoin
に miter が指定されている場合、留め継ぎ( miter )の幅がパスのストロークの太さを大幅に超える可能性がある。
stroke-miterlimit
は、留め幅( miter length - 留め継ぎの外側の角と内側の角との距離)の
stroke-width
に対する限界比率を設定する。この限界を超えた場合、継ぎ目は miter から bevel に転化されなければならない。
When two line segments meet at a sharp angle and miter joins have been specified for 'stroke-linejoin', it is possible for the miter to extend far beyond the thickness of the line stroking the path. The 'stroke-miterlimit' imposes a limit on the ratio of the miter length to the 'stroke-width'. When the limit is exceeded, the join must be converted from a miter to a bevel.
- <miterlimit>
-
留め幅の
stroke-width
に対する限界比率。
<miterlimit>
の値は1以上でなければならない。そうでない値は
サポート外
であり、指定されなかったものとして処理されるものとする。
The limit on the ratio of the miter length to the 'stroke-width'. The value of <miterlimit> must be a number greater than or equal to 1. Any other value shall be treated as unsupported and processed as if the property had not been specified.
留め幅の
stroke-width
に対する比率は、
利用空間
におけるパス区分の継ぎ目がなす角度と直接的な関係があり、次の公式で表される( miterLength を留め幅, theta を継ぎ目がなす角度とする):
The ratio of miter length (distance between the outer tip and the inner corner of the miter) to 'stroke-width' is directly related to the angle (theta) between the segments in user space by the formula:
miterLimit = miterLength / stroke-width = 1 / sin(theta / 2)
例えば限界比率 1.414 においては 90 度より小さい theta に対し bevel が miter にとってかわり、限界比率 4.0 においては約 29 度より小さい theta に対しそうなり、限界比率 10.0 においては約 11.5 度より小さい theta に対しそうなる。
For example, a miter limit of 1.414 converts miters to bevels for theta less than 90 degrees, a limit of 4.0 converts them for theta less than approximately 29 degrees, and a limit of 10.0 converts them for theta less than approximately 11.5 degrees.
このプロパティは要素の
装飾付き包含ボックス
に寄与する。
This property contributes to an element's decorated bounding box.
stroke-dasharray
は、パスのストロークに用いるダッシュと間隔のパターンを指定する。
<list-of-lengths>
はダッシュと間隔の長さを交互に指定するために用いられなければならない
<length>
のリスト。奇数個の値が与えられた場合、偶数個にするために値のリストが繰り返されるものとする。すなわち、 stroke-dasharray="5,3,2" は stroke-dasharray="5,3,2,5,3,2" と同値になる。
stroke-linecap
属性の算出値は各々のダッシュに適用される。ダッシュの長さが0の場合でも、 stroke-linecap の値が round または square ならば先端形状付け( linecap )は追加される。
'stroke-dasharray' specifies the pattern of dashes and gaps that shall be used to stroke paths. The <list-of-lengths> contains the list of <length>s that specify the lengths of alternating dashes and gaps that must be used. If an odd number of values is provided, then the list of values shall be repeated to yield an even number of values. Thus, stroke-dasharray="5,3,2" is equivalent to stroke-dasharray="5,3,2,5,3,2". The computed value of the attribute 'stroke-linecap' is applied to both sides of each dash. If a dash has zero length, linecaps are still added if the stroke-linecap values round and square are used.
- none
-
ダッシュを利用しないことを指示する。ストロークにおける線は一様に描かれなければならない。
Indicates that no dashing shall be used. If stroked, the line must be drawn solid.
- <list-of-lengths>
-
交互に現れるダッシュと間隔の長さに用いられなければならない
<length>
のリスト指定する。負の
<length>
値は
サポート外
として扱うものとし、指定されなかったものとして処理されるものとする。
<length>
の総和が0の場合、ストロークは値 none が指定されていたかのように描画されるものとする。
The list of <length>s that specify the lengths of alternating dashes and gaps that must be used. A negative <length> value shall be treated as unsupported and processed as if the property had not been specified. If the sum of the <length>s is zero, then the stroke shall be rendered as if a value of none were specified.
注記:
stroke-dasharray
の描画のふるまいについて、一部の場合に完全に指定していない。多くの場合、 SVG Tiny の実装はふるまいが決定済みで簡単には変更できない根底のグラフィックスライブラリに依存しているからである。 Example には、ダッシュの端点が2つのパス区分の角にちょうど一致するもの, 部分パスで stroke-dasharray を続けるもの, その他、
stroke-linejoin
と
stroke-linecap
の描画例が含まれている。これらの場合については SVG 1.2 Full の中で完全に指定することや、 linecap とは別に定義される dash-caps のような属性の追加が考えられている。
【ダッシュとパスの先端形状付けを別々の属性で指定することに思われる】
文書作成者には、この仕様で指定していない部分についての
stroke-dasharray
の描画における特定のビューアの特殊なふるまいに依存しないことが奨励される。
Note: Certain cases regarding the behavior of 'stroke-dasharray' are not fully specified because SVG Tiny implementations often rely on underlying graphics libraries with predetermined behaviors they cannot easily change. Examples include: rendering of 'stroke-linejoin' and 'stroke-linecap' in case a dash ends exactly at a corner of two path segments, continuation of stroke-dasharray in subpaths, and others. These cases may be fully specified in version SVG 1.2 Full. Additional attributes, such as dash-caps that can be defined separately from linecaps may be added. Authors are encouraged not to rely on a specific behavior of a specific viewer for 'stroke-dasharray' regarding these currently unspecified cases.
stroke-dashoffset
は、ダッシュの開始に用いられなければならないダッシュパターンまでの距離を指定する。複数個の部分パスを含む
path
要素の描画に際しては、それぞれの部分パスに対し描線を同じ
stroke-dashoffset
の値から開始すべきである。 SVG 1.2 Full ではより厳密な規定や、このふるまいを変更をする属性の追加も考えられている。
'stroke-dashoffset' specifies the distance into the dash pattern that must be used to start the dash. When rendering a 'path' element with multiple subpaths, the value of 'stroke-dashoffset' should start from scratch with the original value of 'stroke-dashoffset' for each subpath. SVG 1.2 Full may be stricter and also add an additional attribute to change this behavior.
-
<length>
-
値は負でもよい。
Values can be negative.
stroke-opacity
は現在のオブジェクトのストロークに用いる不透明度を指示する(
図形とテキストの塗り
を見よ)。
'stroke-opacity' specifies the opacity of the painting operation used to stroke the current object. (See Painting shapes and text.)
-
<opacity-value>
-
現在のオブジェクトのストロークによる塗り操作に用いることになる不透明度。値 0.0 (完全透明)から 1.0 (完全不透明)までの範囲の外の値はこの範囲に切り上げ/下げされる(
特定の範囲への値の切り上げ/下げ
を見よ)。
The opacity of the painting operation that is to be used to stroke the current object. Any values outside the range 0.0 (fully transparent) to 1.0 (fully opaque) must be clamped to this range. (See Clamping values which are restricted to a particular range.)
関連するプロパティ:
fill-opacity
。
Related property: 'fill-opacity'.
11.5 非拡縮ストローク
いかなる変換が適用されてようとオブジェクトの外形線の元の幅が保たれることに関心が持たれる場合がある。例えば地図上の道路が 2px 幅の線で表されているとき、利用者が地図を拡大表示させても道路の 2px 幅が保たれるようにするなど。このような機能を得るため、 SVG Tiny 1.2 では
vector-effect
プロパティが導入されている。将来版の SVG 言語はこのプロパティにより強力なベクター効果を与えることが画策されているが、このバージョンでは非拡縮ストロークのふるまいを指定するに留めている。
Sometimes it is of interest to let the outline of an object keep its original width no matter which transforms are applied to it. For example, in a map with a 2px wide line representing roads it is of interest to keep the roads 2px wide even when the user zooms into the map. To achieve this, SVG Tiny 1.2 introduces the 'vector-effect' property. Future versions of the SVG language will allow for more powerful vector effects through this property but this version restricts it to being able to specify the non-scaling stroke behavior.
-
'vector-effect'
-
| 値: |
non-scaling-stroke | none |
inherit
|
| 初期値: |
none |
| 適用対象: |
グラフィックス要素
|
| 継承: |
しない |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
- none
-
ベクター効果を適用しないことを指示する。すなわち、 SVG 1.1 が利用していた図形の幾何に対し指定した塗りによるフィルを行い、しかる後、指定した塗りによる外形線のストロークを行う既定の描画のふるまいになる。
Specifies that no vector effect shall be applied, i.e. the default rendering behaviour from SVG 1.1 is used which is to first fill the geometry of a shape with a specified paint, then stroke the outline with a specified paint.
- non-scaling-stroke
-
オブジェクトのストロークの仕方を変更する。通常、ストロークには現在の
利用空間
において、図形のパスのストロークの外形線の計算と、その外形線に対しストロークの塗り(単色またはグラデーション)を用いて内部への塗りを行うことが必然的に含まれる。 non-scaling-stroke (非拡縮ストローク)ベクター効果においては、ストローク外形線の計算は利用座標系に代わって「ホスト」座標系において行われるものとする。より正確には:まず UA はホスト座標系を確立する。これは SVG Tiny 1.2 おいては常に「スクリーン座標系」と同値になる。ストローク外形線は次のように算出される:最初に図形のパスがホスト座標系に変換され、次にストローク外形線がホスト座標系で算出される。結果の外形線は
利用座標系
へ逆変換される。(ストローク外形線は常に現在の利用座標系においてストロークの塗りによりフィルされる)。この変更による結果、ストロークの幅は(不均等な拡縮や斜傾変換も含む)要素の変換や拡大率に依存しなくなる。
Modifies the way an object is stroked. Normally stroking involves calculating stroke outline of the shape's path in current user space and filling that outline with the stroke paint (color or gradient). With the non-scaling-stroke vector effect, stroke outline shall be calculated in the "host" coordinate space instead of user coordinate space. More precisely: a user agent establishes a host coordinate space which in SVG Tiny 1.2 is always the same as "screen coordinate space". The stroke outline is calculated in the following manner: first, the shape's path is transformed into the host coordinate space. Stroke outline is calculated in the host coordinate space. The resulting outline is transformed back to the user coordinate system. (Stroke outline is always filled with stroke paint in the current user space). The resulting visual effect of this modification is that stroke width is not dependant on the transformations of the element (including non-uniform scaling and shear transformations) and zoom level.
注記:将来版の SVG にはホスト座標系の制御が考えられている。
Note: Future versions of SVG may allow ways to control the host coordinate system.
下に非拡縮ストローク
vector-effect
の用例を示す。
Below is an example of the non-scaling-stroke 'vector-effect'.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.2" baseProfile="tiny"
width="6cm" height="4cm" viewBox="0 0 600 400"
viewport-fill="rgb(255,150,200)">
<!-- 非拡縮ストロークの例 -->
<desc> Example non-scaling stroke </desc>
<rect x="1" y="1" width="598" height="398" fill="none" stroke="black"/>
<g transform="scale(9,1)">
<line stroke="black" stroke-width="5" x1="10" y1="50" x2="10" y2="350"/>
<line vector-effect="non-scaling-stroke" stroke="black" stroke-width="5"
x1="32" y1="50" x2="32" y2="350"/>
<line vector-effect="none" stroke="black" stroke-width="5"
x1="55" y1="50" x2="55" y2="350"/>
</g>
</svg>
11.6 単純アルファ合成
グラフィックス要素
は
キャンバス
上にすでに描画された要素と単純アルファ合成( simple alpha compositing )を用いて混色( blend )される。結果の
キャンバス
の画素の色と不透明度は次の公式による結果と等しくならなければならない(すべての色値はアルファとの積がとられた値とする):
Graphics elements are blended into the elements already rendered on the canvas using simple alpha compositing, in which the resulting color and opacity at any given pixel on the canvas must be the result of the following formulas (all color values use premultiplied alpha):
Er, Eg, Eb - 要素の色値
Ea - 要素のアルファ値
Cr, Cg, Cb - キャンバスの色値(混色前)
Ca - キャンバスのアルファ値(混色前)
Cr', Cg', Cb' - キャンバスの色値(混色後)
Ca' - キャンバスのアルファ値(混色後)
Ca' = 1 - (1 - Ea) * (1 - Ca)
Cr' = (1 - Ea) * Cr + Er
Cg' = (1 - Ea) * Cg + Eg
Cb' = (1 - Ea) * Cb + Eb
次の描画プロパティは合成演算を行う色空間についての情報を提供し、合成演算に適用される:
The following rendering properties, which provide information about the color space in which to perform the compositing operations, apply to compositing operations:
11.6.1 currentColor 値の合成
currentColor 値には不透明度成分を持つ色値を与え得る。この不透明度値は上で述べたアルファ合成による描画操作に用いられる。すなわち、色を(それ自身も不透明度値を持ち得る)ペイントサーバへ合成する際には currentColor の不透明度値も利用される。
The currentColor value may be assigned a color value that has an opacity component. This opacity value is used in the rendering operation using the alpha compositing method described above. That is, the opacity value in currentColor is used when compositing the color into a paint server (which may have its own values for opacity).
11.7 'viewport-fill' プロパティ
SVG においては文書作成者は
svg
要素など
ビューポート
を確立する任意の要素に対し
ビューポート
へのフィルに用いられる単色を指定できる。
SVG enables the author to specify a solid color which will be used to fill the viewport of any element that creates a viewport, such as the 'svg' element.
viewport-fill
プロパティは
ビューポート
へのフィルに用いる色を確立した要素ごとに指定する。適用された要素の
キャンバス
全体に指定された単色によるフィルが行われなければならない。
キャンバス
はその要素の
viewBox
によりクリッピングされ得る。
The 'viewport-fill' property specifies the color which shall be used to fill the viewport created by a particular element. It must cause the entire canvas of the element that it applies to to be filled with the specified solid color. That canvas may then be clipped by that element's 'viewBox'.
viewport-fill
の値が none の場合、ビューポートへの塗り操作は行われなくなる。
If the value of 'viewport-fill' is none, then no paint operation is applied to the viewport.
下に
viewport-fill
の例を示す:
Below is an example of 'viewport-fill'.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.2" baseProfile="tiny"
viewport-fill="red">
<!-- すべて赤の背景色を持つ。
矩形はフィルされないので、赤い背景色が透過して見えることになる。 -->
<desc>
Everything here has a red background.
The rectangle is not filled, so the red background will show through.
</desc>
<rect x="20" y="20" width="100" height="100" fill="none" stroke="black"/>
</svg>
少し複雑な例を示す。
viewBox
により幅 300 単位, 高さ 100 単位の座標系が与えられる。例の下の画像は
ビューポート
が正方形のときの描画結果を示している。
Here is a slightly more complex example. The 'viewBox' gives a coordinate system 300 units wide and 100 units high. The rendering shows what happens when this is displayed inside a square viewport.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.2" baseProfile="tiny"
viewBox="0 0 300 100" viewport-fill="yellow">
<!-- ビューポートは黄色の背景色を持つ。ビューポートの縦横比が
viewBox と異なる場合、フィルされた矩形のビューポートを覆う
「残りの部分」が黄色の背景になる。 -->
<desc>
The viewport has a yellow background.
The rectangle is filled and covers the viewport, so the yellow
background will only show through in the "leftovers" if the
aspect ratio of the viewport differs from that of the viewBox.
</desc>
<rect x="0" y="0" width="300" height="100" fill="red" fill-opacity="0.3" stroke="black"/>
</svg>
ビューポート
へのフィルは要素の描画過程における最初の操作になる。従って:
The filling of the viewport is the first operation in the rendering chain of an element. Therefore:
-
ビューポートフィル操作はフィルとストロークの前に生じる。
The viewport fill operation happens before filling and stroking.
-
ビューポートフィル操作は合成の前に生じるので、合成操作の入力の一部になる。
The viewport fill operation occurs before compositing, and thus is part of the input to the compositing operations.
-
ビューポートフィル操作は要素の概念的なオフスクリーンバッファへ描画するので不透明度は通常どおり適用される。
The viewport fill operation renders into the element's conceptual offscreen buffer, and thus opacity applies as usual.
-
ビューポートフィルは
fill
または
fill-opacity
プロパティに影響されない。
Viewport fill is not affected by the 'fill' or 'fill-opacity' properties.
11.8 'viewport-fill-opacity' プロパティ
viewport-fill-opacity
プロパティは
viewport-fill
に利用する不透明度を要素ごとに指定する。
The 'viewport-fill-opacity' property specifies the opacity of the 'viewport-fill' that shall be used for a particular element.
- <opacity-value>
-
ビューポート
のフィルによる塗り操作に用いる不透明度。 0.0 (完全透明)から 1.0 (完全不透明)までの範囲の外の値はこの範囲に切り上げ/下げされる(
特定の範囲への値の切り上げ/下げ
を見よ)。
The opacity of the painting operation that is to be used to fill the viewport. Any values outside the range 0.0 (fully transparent) to 1.0 (fully opaque) must be clamped to this range. (See Clamping values which are restricted to a particular range.)
11.9 可視性と描画の制御
SVG は2つのプロパティ
display
と
visibility
を
グラフィックス要素
や(
display
プロパティの場合)
コンテナ要素
の描画の制御に利用する。2つのプロパティのいずれも DOM 内のオブジェクトの有無には影響しない。これらのプロパティの値が何であれ依然としてオブジェクトは DOM に留まる。
SVG uses two properties, 'display' and 'visibility', to control the rendering of graphics elements or (in the case of the 'display' property) container elements. Neither of these two properties affects the objects existence in the DOM, i.e. no matter what value of these properties the object still remains in the DOM.
2つのプロパティの違いは:
The differences between the two properties are as follows:
-
コンテナ要素
に適用される場合、
display
を none に設定するとコンテナとそのすべての子要素は
描画木
から除外される。すなわち要素のグループにグループとして適用される。一方で
visibility
は個別の
グラフィックス要素
にしか適用されない。
g
に対し
visibility
を
hidden
に設定した場合、その子要素はそれ自身の
visibility
プロパティを
visible
に設定していない限りにおいて不可視になる。
When applied to a container element, setting 'display' to none causes the container and all of its children to be excluded from the rendering tree; thus, it acts on groups of elements as a group. 'visibility', however, only applies to individual graphics elements. Setting 'visibility' to hidden on a 'g' will make its children visually invisible as long as the children do not specify their own 'visibility' properties as visible.
-
display
プロパティが
none
に設定された場合、要素は
描画木
の一部になり得ない。しかしながら、
visibility
が
hidden
に設定された場合、要素は
描画木
の一部に存在しているかのように処理され、空間は占めるが実際には
キャンバス
に描画されない。
この違いは
tspan
要素,
イベント処理,
包含ボックスの計算
に影響を及ぼす。
tspan
要素において
display
を
none
に設定した場合、テキストはテキスト配置の目的においては無視される一方、
visibility
を
hidden
に設定した場合、テキストはキャンバスに視覚的に描画されないにもかかわらずテキスト配置には利用される(すなわち空間を占める)。イベントにおいては、(例えばマウスイベントなら)
display
が
none
の場合、要素がイベントを受け取れるためには
描画木
内の存在が要求されるので、要素はイベントを受け取れない一方、
visibility
が
hidden
であっても依然として要素は
pointer-events
プロパティの値に依存してイベントを受け取り得る。
グラフィックス要素
においては、
display
が
none
に設定された場合、要素の幾何は
包含ボックス
の計算に寄与しない一方、
visibility
が
hidden
に設定された場合でも要素の幾何は
包含ボックス
の計算に寄与する。
When the 'display' property is set to none, then the given element does not become part of the rendering tree. With 'visibility' set to hidden, however, processing occurs as if the element were part of the rendering tree and still taking up space, but not actually visually rendered onto the canvas.
This distinction has implications for the 'tspan' element, event processing, and for bounding box calculations.
If 'display' is set to none on a 'tspan' then the text string is ignored for the purposes of text layout; however, if 'visibility' is set to hidden, the text string is used for text layout (i.e., it takes up space) even though it is not visually rendered on the canvas.
Regarding events, if 'display' is set to none, the element receives no events which require the element to be in the rendering tree (for example mouse events); however, if 'visibility' is set to hidden, the element might still receive events, depending on the value of property 'pointer-events'. The geometry of a graphics element with 'display' set to none is not included in bounding box calculations; however, even if 'visibility' is to hidden, the geometry of the graphics element still contributes to bounding box calculations.
-
'display'
-
| 値: |
inline | block | list-item |
run-in | compact | marker |
table |
inline-table | table-row-group | table-header-group |
table-footer-group | table-row | table-column-group | table-column |
table-cell | table-caption | none |
inherit
|
| 初期値: |
inline |
| 適用対象: |
svg,
g,
switch,
a,
foreignObject,
グラフィックス要素
(
テキスト内容ブロック要素
を含む),
メディア要素,
テキスト下位要素(
tspan,
a
など) |
| 継承: |
しない |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
all |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
値 display="none" は、要素とその子要素を直接的に描画しない、あるいは音声を発しないものとすることを指示する(すなわちこれらの要素は
描画木
に存在しない)。 none 以外の算出値は
SVG-UA
が要素を描画するものとすることを指示する。
A value of display="none" indicates that the given element and its children shall not be rendered directly or made audible (i.e., those elements are not present in the rendering tree). Any computed value other than none indicates that the given element shall be rendered or made audible by the SVG user agent.
display
プロパティは要素の直接的描画もしくは音声出力の有無にのみ影響し、要素から要素への参照には影響しない。
The 'display' property only affects the direct rendering or audibility of a given element, whereas it does not prevent elements from being referenced by other elements.
display="none" に設定された要素は、テキスト配置において空間を占めず, イベントは受け取らず,
包含ボックス
の計算にも寄与しない。
Elements with display="none" do not take up space in text layout operations, do not receive events and do not contribute to bounding box calculations.
この仕様で与えられる追加の情報を除き、
このプロパティの正式な定義
は CSS 2
([CSS2], 9.2.5 節)
を参照のこと。
Except for any additional information provided in this specification, the normative definition of this property is found in CSS 2 ([CSS2], section 9.2.5).
- visible
-
対象の
グラフィックス要素
または
メディア要素
が可視であるものとする。
The current graphics element or media element shall be visible.
-
hidden or collapse
-
対象の
グラフィックス要素
または
メディア要素
が不可視であるものとする(すなわち
キャンバス
には何も描画されない)。
The current graphics element or media element shall be invisible (i.e., nothing is painted on the canvas).
display
プロパティとは異なり、
visibility
プロパティは
メディア要素
に対する音声出力の有無には影響しないことに注意。要素の音声出力の有無を制御するためには
display
や
audio-level
プロパティを利用する。
Note that, unlike the 'display' property, the 'visibility' property does not have any affect on the audibility of any media element. To control the audibility of an element, use the 'display' or 'audio-level' properties.
tspan
要素に対し
visibility
プロパティを hidden に設定した場合、テキストは不可視になるにもかかわらず、テキスト配置においては空間を占めるものとする。
Note that if the 'visibility' property is set to hidden on a 'tspan' element, then the text is invisible but shall still takes up space in text layout calculations.
pointer-events
プロパティの値にも依存するが、
visibility
プロパティが
hidden
に設定された
グラフィックス要素
は、イベントを受け取り得る。
Depending on the value of property 'pointer-events', graphics elements which have their 'visibility' property set to hidden still might receive events.
この仕様で与えられる追加の情報を除き、
このプロパティの正式な定義
は CSS 2
([CSS2], 11.2 節)
を参照のこと。
Except for any additional information provided in this specification, the normative definition of this property is found in CSS 2 ([CSS2], section 11.2).
11.10 描画ヒント
11.10.1 color-rendering プロパティ
SVG 内容の作成者にとっては、色の補間と合成における速度と品質のトレードオフに関するヒントを実装に与えたい場合がある。
color-rendering
プロパティは、色の補間と合成演算をどう最適化するかについてのヒントを
SVG-UA
に提供する。
The creator of SVG content might want to provide a hint to the implementation about how to make speed versus quality tradeoffs as it performs color interpolation and compositing. The 'color-rendering' property provides a hint to the SVG user agent about how to optimize its color interpolation and compositing operations.
- auto
-
UA は速度と品質の適切なバランスをとるものとすることを指示するが、速度より品質が重視されるものとする。
Indicates that the user agent shall make appropriate tradeoffs to balance speed and quality, but quality shall be given more importance than speed.
- optimizeSpeed
-
UA は品質より描画速度を優先するものとすることを指示する。 RGB ディスプレイ装置においては、場合によっては UA による色の補間と合成が装置の RGB 色空間で行われることになる。
Indicates that the user agent shall emphasize rendering speed over quality. For RGB display devices, this option will sometimes cause the user agent to perform color interpolation and compositing in the device RGB color space.
- optimizeQuality
-
UA は描画速度より品質を優先するものとすることを指示する。
Indicates that the user agent shall emphasize quality over rendering speed.
11.10.2 shape-rendering プロパティ
SVG 内容の作成者にとっては、
path
要素のようなベクター
グラフィックス要素
や円形や矩形のような
基本図形
の描画に際し何をトレードオフにするかのヒントを実装に与えたい場合がある。
shape-rendering
プロパティがこれらのヒントを提供する。
The creator of SVG content might want to provide a hint to the implementation about what tradeoffs to make as it renders vector graphics elements such as 'path' elements and basic shapes such as circles and rectangles. The 'shape-rendering' property provides these hints.
-
'shape-rendering'
-
| 値: |
auto | optimizeSpeed | crispEdges |
geometricPrecision |
inherit
|
| 初期値: |
auto |
| 適用対象: |
図形
|
| 継承: |
する |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
- auto
-
UA は速度と幾何精度と輪郭の鮮明さとの適切なバランスをとるものとすることを指示するが、速度や輪郭の鮮明さより幾何精度が重視されるものとする。
Indicates that the user agent shall make appropriate tradeoffs to balance speed, crisp edges and geometric precision, but with geometric precision given more importance than speed and crisp edges.
- optimizeSpeed
-
UA は幾何精度と輪郭の鮮明さより速度を優先すべきものとすることを指示する。場合によっては UA による図形のアンチエイリアスがされなくなる。
Indicates that the user agent shall emphasize rendering speed over geometric precision and crisp edges. This option will sometimes cause the user agent to turn off shape anti-aliasing.
- crispEdges
-
UA は描画速度と幾何精度よりアートワークにおける輪郭のコントラストを優先するものとすることを指示する。輪郭の鮮明さを得るため、 UA は垂直または水平に近い直線や曲線に対するアンチエイリアスを行わないようにすることがある。また、 UA は境界が装置の画素に揃うように線の位置と幅を調整することがある。
Indicates that the user agent shall attempt to emphasize the contrast between clean edges of artwork over rendering speed and geometric precision. To achieve crisp edges, the user agent might turn off anti-aliasing for all lines and curves or possibly just for straight lines which are close to vertical or horizontal. Also, the user agent might adjust line positions and line widths to align edges with device pixels.
- geometricPrecision
-
UA は速度と輪郭の鮮明さより幾何精度を優先するものとすることを指示する。
Indicates that the user agent shall emphasize geometric precision over speed and crisp edges.
11.10.3 text-rendering プロパティ
SVG 内容の作成者にとっては、テキスト描画に際し何をトレードオフにするかのヒントを実装に与えたい場合がある。
text-rendering
プロパティがこれらのヒントを提供する。
The creator of SVG content might want to provide a hint to the implementation about what tradeoffs to make as it renders text. The 'text-rendering' property provides these hints.
-
'text-rendering'
-
| 値: |
auto | optimizeSpeed | optimizeLegibility |
geometricPrecision |
inherit
|
| 初期値: |
auto |
| 適用対象: |
テキスト内容ブロック要素 |
| 継承: |
する |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
- auto
-
UA は速度と判読性と幾何精度の適切なバランスをとるものとすることを指示するが、速度と幾何精度より判読性が重視されるものとする。
Indicates that the user agent shall make appropriate tradeoffs to balance speed, legibility and geometric precision, but with legibility given more importance than speed and geometric precision.
- optimizeSpeed
-
UA は幾何精度と判読性より速度を優先するものとすることを指示する。場合によっては UA によるテキストのアンチエイリアスがされなくなる。
Indicates that the user agent shall emphasize rendering speed over legibility and geometric precision. This option will sometimes cause the user agent to turn off text anti-aliasing.
- optimizeLegibility
-
UA は速度と幾何精度より判読性を優先するものとすることを指示する。 UA は最も判読しやすいテキストが生成されるように、アンチエイリアスの技法または組み込みのフォントヒント、あるいはその両方を適用するかどうかを適宜選択する。
Indicates that the user agent shall emphasize legibility over rendering speed and geometric precision. The user agent will often choose whether to apply anti-aliasing techniques, built-in font hinting or both to produce the most legible text.
- geometricPrecision
-
UA は判読性と描画速度より幾何精度を優先するものとすることを指示する。この場合、通常 UA はグリフの外形線がパスデータ描画の幾何精度と同等に描かれるようにするためにフォントヒントを利用しなくなる。
Indicates that the user agent shall emphasize geometric precision over legibility and rendering speed. This option will usually cause the user agent to suspend the use of hinting so that glyph outlines are drawn with comparable geometric precision to the rendering of path data.
11.10.4 image-rendering プロパティ
SVG 内容の作成者にとっては、画像処理における速度と品質のトレードオフに関するヒントを実装に与えたい場合がある。
image-rendering
プロパティは、画像の描画をどのように最適化するかについてのヒントを
SVG-UA
に提供する。
The creator of SVG content might want to provide a hint to the implementation about how to make speed vs. quality tradeoffs as it performs image processing. The 'image-rendering' property provides a hint to the SVG user agent about how to optimize its image rendering.
-
'image-rendering'
-
| 値: |
auto | optimizeSpeed | optimizeQuality |
inherit
|
| 初期値: |
auto |
| 適用対象: |
images |
| 継承: |
する |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
- auto
-
UA は速度と品質の適切なバランスをとるものとすることを指示するが、品質をより重視するものとする。 UA は再標本化アルゴリズムとして、少なくともニアレストネイバー法に相当する品質のものを用いるものとするが、双線型法に相当する品質のものが強く望まれる。
適合高品質 SVG ビューア
においては、 UA は再標本化アルゴリズムとして少なくとも双線型法に相当する品質のものを用いるものとする。
【適合高品質 SVG ビューア - Conforming High-Quality SVG Viewers :この仕様には存在しない SVG 1.1 仕様で定められているもの】
Indicates that the user agent shall make appropriate tradeoffs to balance speed and quality, but quality shall be given more importance than speed. The user agent shall employ a resampling algorithm at least as good as nearest neighbor resampling, but bilinear resampling is strongly preferred. For Conforming High-Quality SVG Viewers, the user agent shall employ a resampling algorithm at least as good as bilinear resampling.
- optimizeQuality
-
UA は描画速度より品質を優先するものとすることを指示する。 UA は再標本化アルゴリズムとして少なくとも双線型法に相当する品質のものを用いるものとする。
Indicates that the user agent shall emphasize quality over rendering speed. The user agent shall employ a resampling algorithm at least as good as bilinear resampling.
- optimizeSpeed
-
UA は品質より描画速度を優先するものとすることを指示する。 UA は再標本化アルゴリズムとして、少なくともニアレストネイバー法に相当する品質以上の、できるだけ高速な描画が得られるものを用いるべきである。より高品質なアルゴリズムで目的の速度が得られるならば、 UA はニアレストネイバー法のかわりにそれを用いるべきである。
Indicates that the user agent shall emphasize rendering speed over quality. The user agent should use a resampling algorithm which achieves the goal of fast rendering, with the requirement that the resampling algorithm shall be at least as good as nearest neighbor resampling. If performance goals can be achieved with higher quality algorithms, then the user agent should use the higher quality algorithms instead of nearest neighbor resampling.
いずれの場合でも、たとえ元のデータあるいは描画対象の装置がインデックスカラーであったとしても、再標本化はトゥルーカラー(例えば24ビット)色空間において行われなければならない。
In all cases, resampling must be done in a truecolor (e.g., 24-bit) color space even if the original data and/or the target device is indexed color.
11.10.5 buffered-rendering プロパティ
SVG 内容の作成者にとっては、要素が変更される頻度に関するヒントを実装に与えて速度とメモリ消費量のトレードオフを調整させられると望ましいことがある。
buffered-rendering
プロパティは、要素の描画バッファをどう最適化するかについてのヒントを
SVG-UA
に提供する。
The creator of SVG content might want to provide a hint to the implementation about how often an element is modified to make speed vs. memory tradeoffs as it performs rendering. The 'buffered-rendering' property provides a hint to the SVG user agent about how to buffer the rendering of elements:
- auto
-
UA は更新の頻度とリソース配分との適度なバランスをとるものと予期されていることを指示する。
Indicates that the user agent is expected to use a reasonable compromise between speed of update and resource allocation.
- dynamic
-
要素は高頻度に変化することが予期されていることを指示する。
Indicates that the element is expected to be modified often.
- static
-
要素の変更頻度が低いと予期されていることを指示する。これは UA にオフスクリーンバッファなどのリソース配分が可能なことを示唆し、再描画のパフォーマンス向上につながる。これは要素が決して変化しないことを意味するものではない。値 'static' のときに要素が変化した場合、再描画によるパフォーマンス低下が生じ得る。
Indicates that the element is not expected to be modified often. This suggests that user agent may be able to allocate resources, such as an offscreen buffer, that would allow increased performance in redraw. It does not mean that the element will never change. If an element is modified when the value is 'static', then redraw might have reduced performance.
11.11 塗りプロパティの継承
この章で述べられている塗りプロパティの値は与えられたオブジェクトの親から継承することができる。しかしながら、塗りの適用は決して
コンテナ要素
(例えば
g
)のレベルではなく、常に各
グラフィックス要素
に対し個別に行われる。例えば次の例では、グラデーションによるフィルが
g
に指定されているが、グラデーションは単に
g
要素を通して各矩形に継承されるだけであり、各々の矩形の内部が個別にグラデーションにより塗られる。
The values of any of the painting properties described in this chapter can be inherited from a given object's parent. Painting, however, is always done on each graphics element individually, never at the container element (e.g., a 'g') level. Thus, for the following SVG, even though the gradient fill is specified on the 'g', the gradient is simply inherited through the 'g' element down into each rectangle, each of which is rendered such that its interior is painted with the gradient.
Example Inheritance
Example Inheritance
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.2" baseProfile="tiny"
width="7cm" height="2cm" viewBox="0 0 700 200">
<!-- グラデーションは末端ノードに適用される -->
<desc> Gradients apply to leaf nodes </desc>
<g>
<defs>
<linearGradient xml:id="MyGradient" gradientUnits="objectBoundingBox">
<stop offset="0" stop-color="#F60"/>
<stop offset="1" stop-color="#FF6"/>
</linearGradient>
</defs>
<rect x="1" y="1" width="698" height="198"
fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2"/>
<g fill="url(#MyGradient)">
<rect x="100" y="50" width="200" height="100"/>
<rect x="400" y="50" width="200" height="100"/>
</g>
</g>
</svg>
オブジェクトの
包含ボックス
に基づいて定義される塗りプロパティは、塗り操作が適用される
グラフィックス要素
の包含ボックスを利用するものとする。
テキスト要素
は、
オブジェクトの包含ボックス
に基づいて定義される塗り操作においては
text
要素全体の包含ボックスを利用するように定義されていることに注意(
オブジェクトの包含ボックス単位とテキスト要素
に関する記述を見よ)。
Any painting properties defined in terms of the object's bounding box use the bounding box of the graphics element to which the operation applies. Note that text elements are defined such that any painting operations defined in terms of the object's bounding box use the bounding box of the entire 'text' element. (See the discussion of object bounding box units and text elements.)
11.12 オブジェクト/グループ不透明度: opacity プロパティ
SVG にはいくつかの不透明度プロパティがある:
There are several opacity properties within SVG:
オブジェクト/グループ不透明度(すぐ下で述べる)を除く他のすべての不透明度プロパティは中間描画演算に絡む。オブジェクト/グループ不透明度は概念的には後処理操作と考えられる。概念的には、オブジェクト/グループが RGBA オフスクリーン画像に描画された後、現在の背景に対する混色の仕方がオブジェクト/グループ不透明度の設定から定められる。
Except for object/group opacity (described just below), all other opacity properties are involved in intermediate rendering operations. Object/group opacity can be thought of conceptually as a postprocessing operation. Conceptually, after the object/group is rendered into an RGBA offscreen image, the object/group opacity setting specifies how to blend the offscreen image into the current background.
オブジェクト/グループ不透明度が
コンテナ要素
に適用された場合、リソースを集中消費する操作になり得る。それ故、このバージョンの SVG ではこのプロパティを
image
要素のみに設定可能かつ適用可能にしている。注記:値を inherit にした場合、不透明度プロパティの初期値 1 が利用され、完全不透明になる。これは指定しなかったのと同じことになる。
Object/group opacity can, if applied to container elements, be a resource intensive operation. Therefore this version of SVG restricts this property to only be set on, and only apply to, the 'image' element. Note: if the value is set to inherit, then the initial value of 1 for the opacity property will be used, meaning full opacity. This is the same as not specifying it at all.
-
<opacity-value>
-
オブジェクト全体に渡って一様に適用されなければならない不透明度設定。 0.0 (完全透明)から 1.0 (完全不透明)までの範囲の外の値はこの範囲に切り上げ/下げされる(
特定の範囲への値の切り上げ/下げ
を見よ)。
The uniform opacity setting that must applied across an entire object. Any values outside the range 0.0 (fully transparent) to 1.0 (fully opaque) must be clamped to this range. (See Clamping values which are restricted to a particular range.)
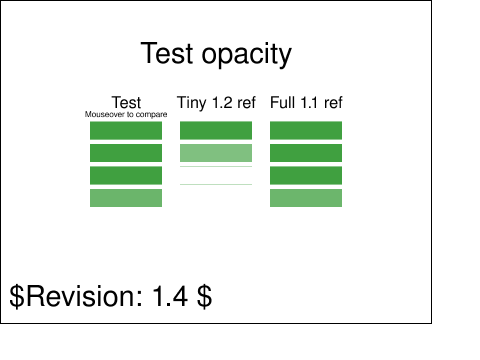
下は SVG Basic/Full 1.1 と SVG Tiny 1.2 におけるふるまいの違いを示す
opacity
の例である。
Below is an example of 'opacity' which illustrates the difference in behavior between SVG Basic/Full 1.1 and SVG Tiny 1.2.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<svg version="1.2" baseProfile="tiny" xml:id="svg-root" width="100%" height="100%"
viewBox="0 0 480 360" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:ev="http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events"
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink">
<!--======================================================================-->
<!--= Copyright 2007 World Wide Web Consortium, (Massachusetts =-->
<!--= Institute of Technology, European Research Consortium for =-->
<!--= Informatics and Mathematics (ERCIM), Keio University). =-->
<!--= All Rights Reserved. =-->
<!--= See http://www.w3.org/Consortium/Legal/. =-->
<!--======================================================================-->
<metadata>
<p>
This test shows the differences in opacity-handling between SVG Tiny 1.2 and SVG Full 1.1.
</p>
<p>
<!-- 左端の列が他の2つの列のいずれかに等しいときテストに合格したことになる。
SVG Tiny 1.2 は SVG 1.1 と 1.2 Tiny の両方を実装する UA より制限された不透明度
の扱いに従うので、要求されるのは中央の列に描かれるものまで。 -->
The test has passed if the leftmost column looks like either of the other two columns.
SVG Tiny 1.2 requires only what is portrayed by the middle column, but does not require
user agents that implement both SVG 1.1 and 1.2 Tiny to follow the more limited
opacity-handling in 1.2 Tiny.
</p>
<p>
<!-- SVG Tiny 1.2 では opacity プロパティは画像要素自身にのみ許容される。
他の場所で遭遇した場合はサポート外の値として扱われなければならない。 -->
In SVG Tiny 1.2 the opacity property is only allowed on the image element itself.
If it's encountered anywhere else it must be treated as an unsupported value.
<!-- 注記:このテストは opacity を image 要素でない要素に用いているので
妥当な 1.2 Tiny ではない。 -->
NOTE: This test is not valid 1.2 Tiny because it's using opacity on something
other than the image element.
</p>
</metadata>
<title xml:id="test-title">$RCSfile: struct-image-201-t.svg,v $</title>
<defs>
<font-face
font-family="SVGFreeSansASCII"
unicode-range="U+0-7F">
<font-face-src>
<font-face-uri xlink:href="SVGFreeSans.svg#ascii"/>
</font-face-src>
</font-face>
</defs>
<g xml:id="test-body-content" font-family="SVGFreeSansASCII,sans-serif" font-size="18">
<text x="240" y="70" text-anchor="middle" font-size="32">Test opacity</text>
<g id="test" transform="translate(-100 0)">
<text x="240" y="120" text-anchor="middle">Test</text>
<text x="240" y="130" text-anchor="middle" font-size="9">Mouseover to compare</text>
<rect id="r1" x="200" y="135" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect id="r2" x="200" y="160" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect id="r3" x="200" y="185" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect id="r4" x="200" y="210" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<g pointer-events="none">
<image width="460" height="20" x="10" y="135" xlink:href="1pixelwhite.png" preserveAspectRatio="none" opacity="0.25"/>
<g opacity="0.5">
<image width="460" height="20" x="10" y="160" xlink:href="1pixelwhite.png" preserveAspectRatio="none" opacity="0.5"/>
<rect id="r5" x="200" y="185" height="20" width="80" fill="white" opacity="0.5"/>
</g>
<g opacity="0.75">
<g opacity="inherit">
<image width="460" height="20" x="10" y="210" xlink:href="1pixelwhite.png" preserveAspectRatio="none" opacity="inherit"/>
</g>
</g>
</g>
<ev:listener event="mouseover" observer="r1" handler="#handler"/>
<ev:listener event="mouseout" observer="r1" handler="#handler"/>
<ev:listener event="mouseover" observer="r2" handler="#handler"/>
<ev:listener event="mouseout" observer="r2" handler="#handler"/>
<ev:listener event="mouseover" observer="r3" handler="#handler"/>
<ev:listener event="mouseout" observer="r3" handler="#handler"/>
<ev:listener event="mouseover" observer="r4" handler="#handler"/>
<ev:listener event="mouseout" observer="r4" handler="#handler"/>
<handler id="handler">
if(event.type == "mouseover")
{
event.target.setFloatTrait("width", 280);
if(event.target.id == "r3")
document.getElementById("r5").setFloatTrait("width", 280);
}
else
{
event.target.setFloatTrait("width", 80);
if(event.target.id == "r3")
document.getElementById("r5").setFloatTrait("width", 80);
}
</handler>
</g>
<g id="tiny12reference">
<text x="240" y="120" text-anchor="middle">Tiny 1.2 ref</text>
<rect x="200" y="135" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect x="200" y="160" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect x="200" y="185" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect x="200" y="210" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect x="200" y="135" height="20" width="80" fill="white" fill-opacity="0.25"/>
<rect x="200" y="160" height="20" width="80" fill="white" fill-opacity="0.5"/>
<rect x="200" y="185" height="20" width="80" fill="white" fill-opacity="1"/>
<rect x="200" y="210" height="20" width="80" fill="white" fill-opacity="1"/>
</g>
<g id="full11reference" transform="translate(100 0)">
<text x="240" y="120" text-anchor="middle">Full 1.1 ref</text>
<rect x="200" y="135" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect x="200" y="160" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect x="200" y="185" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect x="200" y="210" height="20" width="80" fill="green"/>
<rect x="200" y="135" height="20" width="80" fill="white" fill-opacity="0.25"/>
<rect x="200" y="160" height="20" width="80" fill="white" fill-opacity="0.25"/>
<rect x="200" y="185" height="20" width="80" fill="white" fill-opacity="0.25"/>
<rect x="200" y="210" height="20" width="80" fill="white" fill-opacity="0.421875"/>
</g>
</g>
<g font-family="SVGFreeSansASCII,sans-serif" font-size="32">
<text xml:id="revision" x="10" y="340" stroke="none"
fill="black">$Revision: 1.4 $</text>
</g>
<rect xml:id="test-frame" x="1" y="1" width="478" height="358" fill="none" stroke="#000"/>
</svg>
11.13 色
SVG Tiny 1.2 においては、すべての色は sRGB 色空間で指定される
[SRGB]
。 SVG Tiny 1.2 UA は、要求されてはいないが、色管理をサポートしてもよい。しかしながら、 SVG Tiny 1.2 UA はディスプレイシステムの応答曲線が sRGB のそれと異なる場合はガンマ補正を適用すべきである。
In SVG Tiny 1.2, all colors are specified in the sRGB color space [SRGB]. SVG Tiny 1.2 user agents are not required to, but may, support color management. However, SVG Tiny 1.2 user agents should apply gamma correction if the response curve of the display system differs from that of sRGB.
11.13.1 色値の構文
SVG Tiny 1.2 には5つの指定形式があり、適合 SVG インタープリタはいずれもサポートしなければならない:
Five syntactical forms are specified for SVG Tiny 1.2, and all of them must be supported in a conforming SVG Interpreter:
- 3桁 16 進 — #rgb
-
それぞれ 0 〜 F の 16 進数の数字を表し、順に赤, 緑, 青の sRGB 色成分になる。 A 〜 F の数字は大文字でも小文字でもよい。色成分値は 0 は 00 , 1 は 11 , ..., F は FF 等々に置換したものから得られる。この短い書式は 4096 色までしか表現できない。例: #000 (黒) #fff (白) #6CF ( #66CCFF, rgb(102, 204, 255) )。
Each hexadecimal digit, in the range 0 to F, represents one sRGB color component in the order red, green and blue. The digits A to F may be in either uppercase or lowercase. The value of the color component is obtained by replicating digits, so 0 become 00, 1 becomes 11, F becomes FF. This compact syntactical form can represent only 4096 colors. Examples: #000 (i.e. black) #fff (i.e. white) #6CF (i.e. #66CCFF, rgb(102, 204, 255)).
- 6桁 16 進 — #rrggbb
-
それぞれ 0 〜 F の16進数の数字を表し、順に赤, 緑, 青の sRGB 色成分になる。 A 〜 F の数字は大文字でも小文字でもよい。色成分値は 0 は 00 に, 1 は 11 に, ..., F は FF に, 等々と置換したものから得られる。この書式は元々 HTML に導入されたものであり、 16777216 色まで表現できる。例: #9400D3 (暗いすみれ色), #FFD700 (金色)。
Each pair of hexadecimal digits, in the range 0 to F, represents one sRGB color component in the order red, green and blue. The digits A to F may be in either uppercase or lowercase.This syntactical form, originally introduced by HTML, can represent 16777216 colors. Examples: #9400D3 (i.e. a dark violet), #FFD700 (i.e. a golden color).
- 整数関数形式 — rgb(rrr, ggg, bbb)
-
コンマ区切りの各整数は順に赤, 緑, 青に対応する1つの sRGB 成分を表す。コンマの前後の空白は許容される。各整数の範囲は 0 〜 255 。この書式は 16777216 色を表現できる。例: rgb(233, 150, 122) (赤味がかったピンク), rgb(255, 165, 0) (オレンジ色)。
Each integer represents one sRGB color component in the order red, green and blue, separated by a comma and optionally by white space. Each integer is in the range 0 to 255. This syntactical form can represent 16777216 colors. Examples: rgb(233, 150, 122) (i.e. a salmon pink), rgb(255, 165, 0) (i.e. an orange).
- 浮動小数点関数形式 — rgb(R%, G%, B%)
-
コンマ区切りの各百分率値は順に赤, 緑, 青に対応する sRGB 色成分を表す。コンマの前後の空白は許容される。 sRGB 色域の色に対する各成分の範囲は 0.0% 〜 100.0% になり、任意の 10進数を与えられる。科学的記数法はサポートされない。この書式は任意の範囲の色を表現でき、 sRGB の色域も完全にカバーする。1つ以上の色成分の色値の範囲が 0.0% 〜 100.0% の外にある場合は sRGB 色域外の色を表す。例: rgb(12.375%, 34.286%, 28.97%) 。
Each percentage value represents one sRGB color component in the order red, green and blue, separated by a comma and optionally by white space. For colors inside the sRGB gamut, the range of each component is 0.0% to 100.0% and an arbitrary number of decimal places may be supplied. Scientific notation is not supported. This syntactical form can represent an arbitrary range of colors, completely covering the sRGB gamut. Color values where one or more components are below 0.0% or above 100.0% represent colors outside the sRGB gamut Examples: rgb(12.375%, 34.286%, 28.97%).
- 色キーワード
-
下に示す 16 個の色キーワード(元来は HTML 4
[HTML4]
のものだが)はサポートされなければならない。また、すべて小文字でなければならない。
The sixteen color keywords below (originally from HTML 4 [HTML4]) must be supported, with the further restriction that they must be lowercase.
11.13.2 HTML 色キーワード
 |
black |
rgb(0, 0, 0) |
 |
green |
rgb(0, 128, 0) |
 |
silver |
rgb(192, 192, 192) |
 |
lime |
rgb(0, 255, 0) |
 |
gray |
rgb(128, 128, 128) |
 |
olive |
rgb(128, 128, 0) |
 |
white |
rgb(255, 255, 255) |
 |
yellow |
rgb(255, 255, 0) |
 |
maroon |
rgb(128, 0, 0) |
 |
navy |
rgb(0, 0, 128) |
 |
red |
rgb(255, 0, 0) |
 |
blue |
rgb(0, 0, 255) |
 |
purple |
rgb(128, 0, 128) |
 |
teal |
rgb(0, 128, 128) |
 |
fuchsia |
rgb(255, 0, 255) |
 |
aqua |
rgb(0, 255, 255) |
11.14 ペイントサーバ
SVG においては、次のいずれかを用いて
図形
とテキストに対しフィル(fill - 内部への塗り)とストローク(stroke - 外形線への塗り)ができる:
With SVG, you can fill (i.e., paint the interior of) or stroke (i.e., paint the outline of) shapes and text using one of the following:
SVG はペイントサーバ( paint server )という概念を用いる。グラデーションとパターンは単に組み込みの特定の種類のペイントサーバの一種になる。
solidColor
要素は別の組み込みのペイントサーバであり、
色
で述べられている。
SVG uses the general notion of a paint server. Gradients and patterns are just specific types of built-in paint servers. The 'solidColor' element is another built-in paint server, described in Color.
システムペイントは別として、ペイントサーバは
fill
あるいは
stroke
プロパティから
局所 IRI 参照
を用いて参照される。
Apart from system paint, paint servers are referenced using a local IRI reference on a 'fill' or 'stroke' property.
11.14.1 システムペイントサーバ
以下に挙げるシステムペイントサーバはサポートされなければならない。
塗りの指定
でシステムペイントサーバのいずれかが指定された場合、 UA はシステムが提供するペイントサーバを利用するか、あるいは色やグラデーションなどの置換ペイントサーバを用いて塗りを行わなければならない。多くの場合、システムペイントサーバは OS, 利用者の選択, 実装に依存する。置換ペイントサーバは利用者の色選択を含むプラットフォームのユーザインターフェース構成要素の見かけに相応しいものにすべきである。満足なシステムペイントサーバ API を提供しない環境においては、適合 UA は必ずしも環境のシステムペイントサーバに合わせる必要の無い相応しいペイントサーバで代用してもよい。
The following list of system paint servers must be supported. If a paint specification specifies one of the system paint servers, then the user agent must either paint using a system-provided paint server or paint with a substitute paint server, such as a color or gradient. System paint servers often depend on the operating system, user choices, and the implementation. Substitute paint servers should attempt to match the appearance of corresponding user interface elements on the platform, including user color choices. In environments which do not provide adequate system paint server APIs, a conformant user agent may use substitute paint servers which do not necessarily match the environment's system paint servers.
塗りにシステムペイントを指定した場合の算出値は指定値になる。
The computed value of a paint specified as a system paint is the specified value.
-
ActiveBorder
-
アクティブウィンドウの境界。
Active window border.
-
ActiveCaption
-
アクティブウィンドウのキャプション【タイトルバー】。
Active window caption.
-
AppWorkspace
-
複数文書インターフェースの背景色。
Background color of multiple document interface.
-
Background
-
デスクトップ背景。
Desktop background.
-
ButtonFace
-
3次元的表示部品の表色。
Face color for three-dimensional display elements.
-
ButtonHighlight
-
3次元的表示部品の暗い影(光源から離れた側の境界)。
Dark shadow for three-dimensional display elements (for edges facing away from the light source).
-
ButtonShadow
-
3次元的表示部品の影色。
Shadow color for three-dimensional display elements.
-
ButtonText
-
ボタンのテキスト。
Text on push buttons.
-
CaptionText
-
キャプション, サイズボックス, スクロールバーボックスのテキスト。
Text in caption, size box, and scrollbar arrow box.
-
GrayText
-
無効化された(薄暗い)テキスト。
Disabled ('grayed') text.
-
Highlight
-
コントロールで選択されている項目。
Item(s) selected in a control.
-
HighlightText
-
コントロールで選択されているテキスト。
Text of item(s) selected in a control.
-
InactiveBorder
-
アクティブでないウィンドウ境界。
Inactive window border.
-
InactiveCaption
-
アクティブでないウィンドウのキャプション。
Inactive window caption.
-
InactiveCaptionText
-
アクティブでないキャプション内のテキスト色。
Color of text in an inactive caption.
-
InfoBackground
-
ツールチップの背景色。
Background color for tooltip controls.
-
InfoText
-
ツールチップのテキスト色。
Text color for tooltip controls.
-
Menu
-
メニュー背景。
Menu background.
-
MenuText
-
メニューのテキスト。
Text in menus.
-
Scrollbar
-
スクロールバーの灰色領域。
Scroll bar gray area.
-
ThreeDDarkShadow
-
3次元的表示部品の暗い影。
Dark shadow for three-dimensional display elements.
-
ThreeDFace
-
3次元的表示部品の表色。
Face color for three-dimensional display elements.
-
ThreeDHighlight
-
3次元的表示部品のハイライト色。
Highlight color for three-dimensional display elements.
-
ThreeDLightShadow
-
3次元的表示部品の明色(光源側の境界)。
Light color for three-dimensional display elements (for edges facing the light source).
-
ThreeDShadow
-
3次元的表示部品の影。
Dark shadow for three-dimensional display elements.
-
Window
-
ウィンドウ背景。
Window background.
-
WindowFrame
-
ウィンドウ枠。
Window frame.
-
WindowText
-
ウィンドウ内のテキスト。
Text in windows.
11.14.2 solidColor 要素
solidColor
要素は不透明度付きの単色を与えるペイントサーバである。他のペイントサーバ(グラデーション等)同様に他から参照させられる。
The 'solidColor' element is a paint server that provides a single color with opacity. It can be referenced like the other paint servers (i.e. gradients).
solid-color
プロパティはこの
solidColor
要素に利用する色を指定する。キーワード currentColor を
fill
と
stroke
プロパティに対する
<paint>
の指定と同じように指定できる。
The 'solid-color' property specifies the color that shall be used for this 'solidColor' element. The keyword currentColor can be specified in the same manner as within a <paint> specification for the 'fill' and 'stroke' properties.
-
'solid-color'
-
| 値: |
currentColor |
<color> | inherit |
| 初期値: |
black |
| 適用対象: |
solidColor 要素 |
| 継承: |
しない |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、<color> 指定値 |
solid-opacity
プロパティは
solidColor
の不透明度を定める。
The 'solid-opacity' property defines the opacity of the 'solidColor'.
-
'solid-opacity'
-
| 値: |
<opacity-value> | inherit
|
| 初期値: |
1 |
| 適用対象: |
solidColor 要素 |
| 継承: |
しない |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
- <opacity-value>
-
solidColor
の不透明度。 0.0 (完全透明)から 1.0 (完全不透明)までの範囲の外の値はこの範囲に切り上げ/下げられなければならない(
特定の範囲への値の切り上げ/下げ
を見よ)。
The opacity of the 'solidColor'. Any values outside the range 0.0 (fully transparent) to 1.0 (fully opaque) must be clamped to this range. (See Clamping values which are restricted to a particular range.)
solidColor
ペイントサーバは
solid-opacity
で定めた不透明度を用いて指定された色の塗りを適用する。
solid-opacity
の値は
fill
や
stroke
による塗りの描画に利用される不透明度とは独立である(
アルファ合成
を見よ)。
The 'solidColor' paint server applies paint of the specified color using the opacity defined in 'solid-opacity'. The value of 'solid-opacity' is independent of the opacity used to render the paint via 'fill' or 'stroke' (see alpha compositing).
プロパティ
は先祖要素から
solidColor
要素に継承するものとする。プロパティは
solidColor
要素を参照する要素からは継承しないものとする。
Properties shall inherit into the 'solidColor' element from its ancestors; properties shall not inherit from the element referencing the 'solidColor' element.
solidColor
要素は決して直接描画されることはなく、
fill
あるいは
stroke
プロパティからの参照以外に使い道はない。
display
プロパティは
solidColor
要素に適用されない。すなわち、
solidColor
要素は
display
プロパティの値が none 以外であっても直接描画されることはなく、たとえ要素自身あるいはその先祖において
display
プロパティの値が none であっても参照による利用は可能である。
'solidColor' elements are never rendered directly; their only usage is as something that can be referenced using the 'fill' and 'stroke' properties. The 'display' property does not apply to the 'solidColor' element; thus, 'solidColor' elements are not directly rendered even if the 'display' property is set to a value other than none, and 'solidColor' elements are available for referencing even when the 'display' property on the 'solidColor' element or any of its ancestors is set to none.
下に
solidColor
要素の例を示す:
Below is an example of the 'solidColor' element:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink"
version="1.2" baseProfile="tiny"
width="480" height="360" viewBox="0 0 480 360">
<title>'solidColor' example</title>
<defs>
<solidColor xml:id="solidMaroon" solid-color="maroon" solid-opacity="0.7"/>
</defs>
<g>
<circle transform="translate(100, 150)" fill="url(#solidMaroon)" r="30"/>
<rect fill="url(#solidMaroon)" transform="translate(190, 150)" x="-30" y="-30" width="60" height="60"/>
<path fill="url(#solidMaroon)" transform="translate(270, 150)" d="M 0 -30 L 30 30 L -30 30 Z" />
<text fill="url(#solidMaroon)" transform="translate(340, 150)" y="21" font-weight="bold" font-size="60">A</text>
</g>
</svg>
11.14.3 color プロパティ
CSS2 においてテキストの色として定められている
color
プロパティは SVG 要素には直接適用されない。しかしながら、 SVG color プロパティの値を currentColor キーワードが利用できるプロパティ:
fill,
stroke,
solid-color,
stop-color
プロパティに間接的な値を与えるために利用してもよい。
The 'color' property, which is defined in CSS2 as the color of text, does not directly apply to SVG elements. The value of the SVG color property may however be used to provide an indirect value for those properties which allow the currentColor keyword: the 'fill', 'stroke', 'solid-color' and 'stop-color' properties.
-
'color'
-
| 値: |
<color> |
inherit
|
| 初期値: |
UA に依存 |
| 適用対象: |
なし。 currentColor を介して他のプロパティに間接的に働く
|
| 継承: |
する |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、<color> 指定値 |
この仕様で与えられる追加の情報を除き、
このプロパティの正式な定義
は CSS 2
([CSS2], 14.1 節)
を参照のこと。
Except for any additional information provided in this specification, the normative definition of the property is found in CSS 2 ([CSS2], section 14.1).
11.15 グラデーション
グラデーションとはベクトルに沿った色から色への滑らかで連続的な色の変化である。同じベクトルに沿って更に別の色へと変化させることも可能である。 SVG では2種類のグラデーション
linearGradient
と
radialGradient
が提供される。
Gradients consist of continuously smooth color transitions along a vector from one color to another, possibly followed by additional transitions along the same vector to other colors. SVG provides for two types of gradients, 'linearGradient' and 'radialGradient'.
一旦定義されたグラデーションは
グラフィックス要素
の
fill
や
stroke
プロパティから参照され得るようになる。このとき、要素のフィルやストローク(同順)は参照先のグラデーションにより行われるものとする。
Once defined, gradients are then referenced using 'fill' or 'stroke' properties on a given graphics element to indicate that the given element shall be filled or stroked with the referenced gradient.
11.15.1 線型グラデーション
線型グラデーションは
linearGradient
要素で定義される。
Linear gradients are defined by a 'linearGradient' element.
属性定義:
-
gradientUnits =
"userSpaceOnUse" | "objectBoundingBox"
グラデーションの描画に用いるものとする属性
'x1',
'y1',
'x2',
'y2'
の座標系を定義する。
Defines the coordinate system for attributes 'x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2' that shall be used when rendering the gradient.
gradientUnits="userSpaceOnUse" の場合、
'x1',
'y1',
'x2',
'y2'
は、グラデーション要素が参照された時点における現在の
利用座標系
(すなわち
fill
または
stroke
プロパティによりグラデーション要素を参照している要素の利用座標系)の値を表すものとする。
If gradientUnits="userSpaceOnUse", 'x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2' shall represent values in the coordinate system that results from taking the current user coordinate system in place at the time when the gradient element is referenced (i.e., the user coordinate system for the element referencing the gradient element via a 'fill' or 'stroke' property).
gradientUnits="objectBoundingBox" の場合、属性
'x1',
'y1',
'x2',
'y2'
の利用座標系はグラデーションが適用される要素の
包含ボックス
を用いて確立されるものとする(
オブジェクトの包含ボックス単位
を見よ)。
If gradientUnits="objectBoundingBox", the user coordinate system for attributes 'x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2' shall be established using the bounding box of the element to which the gradient is applied (see Object bounding box units).
gradientUnits="objectBoundingBox" の場合、線型グラデーションの筋目はオブジェクトの包含ボックス空間(すなわち (0,0) がオブジェクトの包含ボックスの左上隅, (1,1) が右下隅に対応する抽象的な座標系)においてはグラデーションベクトルに対し垂直になるものとする。オブジェクトの包含ボックスが正方形でない場合、包含ボックス空間から利用空間へは不均等な拡縮変換が適用されるので、この概念的な包含ボックス空間においてグラデーションベクトルに垂直な筋目は、利用空間においてはグラデーションベクトルに対し垂直にならない形に描画されることになる。
When gradientUnits="objectBoundingBox" the stripes of the linear gradient shall be perpendicular to the gradient vector in object bounding box space (i.e., the abstract coordinate system where (0,0) is at the top/left of the object bounding box and (1,0) is at the top/right of the object bounding box). When the object's bounding box is not square, the stripes that are conceptually perpendicular to the gradient vector within object bounding box space shall render non-perpendicular relative to the gradient vector in user space due to application of the non-uniform scaling transformation from bounding box space to user space.
省略値
は 'objectBoundingBox' 。
The lacuna value is 'objectBoundingBox'.
アニメーション:可
-
x1 = "<coordinate>"
'x1',
'y1',
'x2',
'y2'
は、線型グラデーションの
グラデーションストップ
が写像されるものとする始点と終点を与えるグラデーションベクトルを定義する。
'x1',
'y1',
'x2',
'y2'
の値は実数でなければならない。
'x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2' define a gradient vector for the linear gradient. This gradient vector provides starting and ending points onto which the gradient stops shall be mapped. The values of 'x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2' must be numbers.
省略値
は '0' 。
The lacuna value is '0'.
アニメーション:可
-
y1 = "<coordinate>"
x1
を見よ。
See 'x1'.
省略値
は '0' 。
The lacuna value is '0'.
アニメーション:可
-
x2 = "<coordinate>"
x1
を見よ。
See 'x1'.
省略値
は '1' 。
The lacuna value is '1'.
アニメーション:可
-
y2 = "
<coordinate>"
- See
x1.
省略値
は '0' 。
The lacuna value is '0'.
アニメーション:可
x1 =
x2,
y1 =
y2
の場合、最後の
グラデーションストップ
の色と不透明度を用いた単色で領域が塗られるものとする。
If 'x1' = 'x2' and 'y1' = 'y2', then the area to be painted shall be painted as a single color using the color and opacity of the last gradient stop.
グラデーションが対象の矩形の内側で開始または終了する場合、残りの対象領域はグラデーションの末端の色を利用してフィルされるものとする。
If the gradient starts or ends inside the bounds of the target rectangle the terminal colors of the gradient shall be used to fill the remainder of the target region.
プロパティ
は先祖要素から
linearGradient
要素に継承するものとする。プロパティは
linearGradient
要素を参照する要素からは継承しないものとする。
Properties shall inherit into the 'linearGradient' element from its ancestors; properties shall not inherit from the element referencing the 'linearGradient' element.
linearGradient
要素は決して直接描画されることはなく、
fill
あるいは
stroke
プロパティからの参照以外に使い道はない。
display
プロパティは
linearGradient
要素に適用されない。すなわち、
linearGradient
要素は
display
プロパティの値が none 以外であっても直接描画されることはなく、たとえ要素自身あるいはその先祖において
display
プロパティの値が none であっても参照による利用は可能である。
'linearGradient' elements are never rendered directly; their only usage is as something that can be referenced using the 'fill' and 'stroke' properties. The 'display' property does not apply to the 'linearGradient' element; thus, 'linearGradient' elements are not directly rendered even if the 'display' property is set to a value other than none, and 'linearGradient' elements are available for referencing even when the 'display' property on the 'linearGradient' element or any of its ancestors is set to none.
Example 13_01 に線型グラデーション・ペイントサーバの参照による矩形のフィルを示す。
Example 13_01 shows how to fill a rectangle by referencing a linear gradient paint server.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.2" baseProfile="tiny"
width="8cm" height="4cm" viewBox="0 0 800 400">
<!-- 線型グラデーション・ペイントサーバによる矩形のフィル -->
<desc>Example 13_01 - fill a rectangle using a linear gradient paint server </desc>
<g>
<defs>
<linearGradient xml:id="MyGradient">
<stop offset="0.05" stop-color="#F60"/>
<stop offset="0.95" stop-color="#FF6"/>
</linearGradient>
</defs>
<!-- 描画領域の枠を青色にする -->
<!-- Outline the drawing area in blue -->
<rect fill="none" stroke="blue"
x="1" y="1" width="798" height="398"/>
<!-- 矩形の内部は線型グラデーション・ペイントサーバを用いて塗られる -->
<!-- The rectangle is filled using a linear gradient paint server -->
<rect fill="url(#MyGradient)" stroke="black" stroke-width="5"
x="100" y="100" width="600" height="200"/>
</g>
</svg>
11.15.2 放射型グラデーション
放射型グラデーション
radialGradient
要素で定義される。
Radial gradients are defined by a 'radialGradient' element.
属性定義:
- gradientUnits = "userSpaceOnUse" | "objectBoundingBox"
グラデーションの描画に用いるものとする属性
cx,
cy,
r
の座標系を定義する。
Defines the coordinate system for attributes 'cx', 'cy', 'r' that shall be used when rendering the gradient.
gradientUnits="userSpaceOnUse" の場合、
cx,
cy,
r
はグラデーション要素が参照された時点における現在の利用座標系(すなわち
fill
または
stroke
プロパティによりグラデーション要素を参照している要素の利用座標系)の値を表すものとする。
If gradientUnits="userSpaceOnUse", 'cx', 'cy', 'r' shall represent values in the coordinate system that results from taking the current user coordinate system in place at the time when the gradient element is referenced (i.e., the user coordinate system for the element referencing the gradient element via a 'fill' or 'stroke' property).
gradientUnits="objectBoundingBox" の場合、属性
cx,
cy,
r
の利用座標系はグラデーションが適用される要素の
包含ボックス
を用いて確立されるものとする(
オブジェクトの包含ボックス単位
を見よ)。
If gradientUnits="objectBoundingBox", the user coordinate system for attributes 'cx', 'cy', 'r' shall be established using the bounding box of the element to which the gradient is applied (see Object bounding box units).
gradientUnits="objectBoundingBox" の場合、放射型グラデーションの輪はオブジェクトの包含ボックス空間(すなわち (0,0) がオブジェクトの包含ボックスの左上隅、(1,1) が右下隅に対応する抽象的な座標系)において真円になるものとする。オブジェクトの包含ボックスが正方形でない場合、包含ボックス空間から利用空間への不均等な拡縮変換が適用されるので、この包含ボックス空間において概念的に真円の輪は、利用空間においては楕円形に描画されることになる。
When gradientUnits="objectBoundingBox" the rings of the radial gradient shall be circular with respect to the object bounding box space (i.e., the abstract coordinate system where (0,0) is at the top/left of the object bounding box and (1,1) is at the bottom/right of the object bounding box). When the object's bounding box is not square, the rings that are conceptually circular within object bounding box space shall render as elliptical due to application of the non-uniform scaling transformation from bounding box space to user space.
省略値
は 'objectBoundingBox' 。
The lacuna value is 'objectBoundingBox'.
アニメーション:可
-
cx = "<coordinate>"
cx,
cy,
r
は放射型グラデーションに対する最大の(すなわち最外縁の)円を定義する。
グラデーションストップ
の 0 は
(cx,
cy)
へ写像される。
'cx', 'cy' and 'r' define the largest (i.e., outermost) circle for the radial gradient and the 0 gradient stop is mapped to ('cx', 'cy').
省略値
は '0.5' 。
The lacuna value is '0.5'.
アニメーション:可
-
cy = "<coordinate>"
cx.
を見よ。
See 'cx'.
省略値
は '0.5' 。
The lacuna value is '0.5'.
アニメーション:可
-
r = "<length>"
cx.
を見よ。
See 'cx'.
負値は
サポート外
として扱われるものとする。値を0にすると、最後の
グラデーションストップ
の色と不透明度を用いた単色で領域が塗られるものとする。
省略値
は '0.5' 。
A negative value shall be treated as unsupported. A value of zero shall cause the area to be painted as a single color using the color and opacity of the last gradient stop. The lacuna value is '0.5'.
アニメーション:可
グラデーションが塗り対象のオブジェクトの境界内で開始または終了する場合、残りの対象領域はグラデーションの末端の色を利用してフィルされるものとする。
If the gradient starts or ends inside the bounds of the object(s) being painted by the gradient the terminal colors of the gradient shall be used to fill the remainder of the target region.
プロパティ
は先祖要素から
radialGradient
要素に継承するものとする。プロパティは
radialGradient
要素を参照する要素からは継承しないものとする。
Properties shall inherit into the 'radialGradient' element from its ancestors; properties shall not inherit from the element referencing the 'radialGradient' element.
radialGradient
要素は決して直接描画されることはなく、
fill
あるいは
stroke
プロパティからの参照以外の使い道はない。
display
プロパティは
radialGradient
要素に適用されない。すなわち、
radialGradient
要素は
display
プロパティの値が none 以外であっても直接描画されることはなく、たとえ要素自身あるいはその先祖において
display
プロパティの値が none であっても参照による利用は可能である。
'radialGradient' elements must never be rendered directly; their only usage is as something that can be referenced using the 'fill' and 'stroke' properties. The 'display' property does not apply to the 'radialGradient' element; thus, 'radialGradient' elements are not directly rendered even if the 'display' property is set to a value other than none, and 'radialGradient' elements are available for referencing even when the 'display' property on the 'radialGradient' element or any of its ancestors is set to none.
Example 13_02 に放射型グラデーション・ペイントサーバの参照による矩形のフィルを示す。
Example 13_02 shows how to fill a rectangle by referencing a radial gradient paint server.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.2" baseProfile="tiny"
width="8cm" height="4cm" viewBox="0 0 800 400">
<!-- 放射型グラデーション・ペイントサーバによる矩形のフィル -->
<desc>Example 13_02 - fill a rectangle by referencing a radial gradient paint server </desc>
<g>
<defs>
<radialGradient xml:id="MyGradient" gradientUnits="userSpaceOnUse"
cx="400" cy="200" r="300">
<stop offset="0" stop-color="red"/>
<stop offset="0.5" stop-color="blue"/>
<stop offset="1" stop-color="red"/>
</radialGradient>
</defs>
<!-- 描画領域の枠を青色にする -->
<!-- Outline the drawing area in blue -->
<rect fill="none" stroke="blue"
x="1" y="1" width="798" height="398"/>
<!-- 矩形の内部は放射型グラデーション・ペイントサーバを用いて塗られる -->
<!-- The rectangle is filled using a radial gradient paint server -->
<rect fill="url(#MyGradient)" stroke="black" stroke-width="5"
x="100" y="100" width="600" height="200"/>
</g>
</svg>
11.15.3 グラデーションストップを定める:stop 要素
linearGradient
要素や
radialGradient
要素によるグラデーションに用いられる色の勾配はその子要素の
stop
要素で定義される。
The ramp of colors to use on a gradient is defined by the 'stop' elements that are child elements to either the 'linearGradient' element or the 'radialGradient' element.
属性定義:
- offset = "<number>"
グラデーションストップの位置を指示する。線型グラデーションの場合、
offset
属性は グラデーションベクトル の方向に沿う位置を表す。放射型グラデーションの場合、
(cx,
cy)
から最大/再外縁の円周までの相対距離を表す。
The 'offset' attribute is a <number> which indicates where the gradient stop shall be placed. For linear gradients, the 'offset' attribute represents a location along the gradient vector. For radial gradients, it represents a relative distance from ('cx', 'cy') to the edge of the outermost/largest circle.
省略値
は '0' 。
The lacuna value is '0'.
アニメーション:可
stop-color
プロパティはグラデーションストップに用いるものとする色を指定する。キーワード currentColor を
fill
や
stroke
プロパティに対する
<paint>
の指定と同じように指定できる。
The 'stop-color' property specifies the color that shall be used at the gradient stop. The keyword currentColor can be specified in the same manner as within a <paint> specification for the 'fill' and 'stroke' properties.
-
'stop-color'
-
| 値: |
currentColor |
<color> |
inherit |
| 初期値: |
black |
| 適用対象: |
stop 要素 |
| 継承: |
しない |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、<color> 指定値 |
stop-opacity
プロパティはグラデーション
stop
に用いるものとする不透明度を指定する。
The 'stop-opacity' property specifies the opacity that shall be used for the gradient 'stop'.
-
'stop-opacity'
-
| 値: |
<opacity-value> |
inherit |
| 初期値: |
1 |
| 適用対象: |
stop 要素 |
| 継承: |
しない |
| 百分率: |
N/A |
| メディア: |
visual |
| アニメーション: |
可 |
| 算出値: |
inherit を除き、指定値 |
グラデーション・ペイントサーバは
stop-opacity
で定められる不透明度を用いて指定されたグラデーションによる塗りを適用する。
stop-opacity
の値は
fill
や
stroke
による塗りの描画で利用される不透明度とは独立になる(
アルファ合成
を見よ)。
The gradient paint server applies paint of the specified gradient using the opacities defined by 'stop-opacity' values. The values of 'stop-opacity' are independent of the opacity used to render the paint via 'fill' or 'stroke' (see alpha compositing).
-
<opacity-value>
-
現在のグラデーション
stop
に対する
stop-color
の不透明度。 0.0 (完全透明)から 1.0 (完全不透明)までの範囲の外の値はこの範囲に切り上げ/下げされる(
特定の範囲への値の切り上げ/下げ
を見よ)。
The opacity of the 'stop-color' for the current gradient 'stop'. Any values outside the range 0.0 (fully transparent) to 1.0 (fully opaque) must be clamped to this range. (See Clamping values which are restricted to a particular range.)
グラデーションにおけるいくつかの注意:
Some notes on gradients:
0.0 から 1.0 の範囲外のグラデーションの offset 値は この範囲に切り上げ/下げられなければならない(
特定の範囲制限のある値の切り上げ/下げ
を見よ)。
Any gradient offset values outside the range 0.0 to 1.0 must be clamped to this range. (See Clamping values which are restricted to a particular range.)
グラデーションの効果が得られるようにするためには少なくとも2つ以上の
stop
が定義されている必要がある。
stop
が定義されていない場合、塗りの指定に 'none' が設定されたものとして塗りが行われるものとする。
stop
が一つだけ指定されている場合、そのグラデーションストップで定義されている色による一様な塗りが行われるものとする。
It is necessary that at least two 'stop' elements are specified to have a gradient effect. If no 'stop' elements are specified, then painting shall occur as if none were specified as the paint style. If one 'stop' is specified, then painting shall occur with the solid color fill using the color defined for that gradient stop.
グラデーションにおける各グラデーションストップの offset 値は前の offset 値以上でなければならない。もし offset 値が前に現れる offset 値のいずれかより小さい場合、その offset 値はそれら offset 値の最大値に調整されなければならない。
Each gradient offset value is required to be equal to or greater than the previous gradient stop's offset value. If a given gradient stop's offset value is not equal to or greater than all previous offset values, then the offset value must be adjusted to be equal to the largest of all previous offset values.
2つのグラデーションストップが同じ offset 値を持つ場合、後の方のグラデーションストップが境目から後の色を制御するものとする。特に:
If two gradient stops have the same offset value, then the latter gradient stop shall control the color value at the overlap point. In particular:
<stop offset="0" stop-color="white"/>
<stop offset=".2" stop-color="red"/>
<stop offset=".2" stop-color="blue"/>
<stop offset="1" stop-color="black"/>
の効果はほぼ次と同じである:
will have approximately the same effect as:
<stop offset="0" stop-color="white"/>
<stop offset=".1999999999" stop-color="red"/>
<stop offset=".2" stop-color="blue"/>
<stop offset="1" stop-color="black"/>
すなわち、グラデーションは白から赤へ滑らかに移行し、急激に赤から青に変移し、青から黒へ滑らかに移行する。
which is a gradient that goes smoothly from white to red, then abruptly shifts from red to blue, and then goes smoothly from blue to black.
色と不透明度の補間は別々に行われ、結果のグラデーションは
単純アルファ合成
を用いて合成される。例えば:
Colors and opacities are interpolated separately, and the resulting gradient is composited using simple alpha compositing. In particular:
<stop offset="0" stop-color="#F00" stop-opacity="0"/>
<stop offset="1" stop-color="#0F0" stop-opacity="1"/>
の生成結果は、完全に透明な赤, 半透明で暗い黄, 完全に不透明な黄緑へと変化するグラデーションになる。
will produce a gradient from fully transparent red, via partly transparent dark yellow, to fully opaque lime.
すべてのグラデーションストップは補間色空間( interpolation color space )に変換されなければならない。グラデーションストップ色の色補間は補間色空間にて行われなければならない。
All gradient stops must be converted into the interpolation color space. Interpolation between gradient stop colors must occur in the interpolation color space.
SVG Tiny 1.2 UA は補間グラデーションを sRGB または linearRGB 色空間のいずれで行ってもよい。いずれの色域も同じ色再現域( color gamut )を持つ(
[SRGB]
参照)。
SVG Tiny 1.2 user agents have the option to interpolate gradients in either sRGB or in linearRGB color space. Both color spaces have the same color gamut (see [SRGB]).
他の W3C 仕様が別の補間色空間の指定を許容する可能性もある。
Other W3C specifications may allow alternative interpolation color spaces to be specified.